Planting Methods, Rates, and Dates
go.ncsu.edu/readext?1015325
en Español / em Português
El inglés es el idioma de control de esta página. En la medida en que haya algún conflicto entre la traducción al inglés y la traducción, el inglés prevalece.
Al hacer clic en el enlace de traducción se activa un servicio de traducción gratuito para convertir la página al español. Al igual que con cualquier traducción por Internet, la conversión no es sensible al contexto y puede que no traduzca el texto en su significado original. NC State Extension no garantiza la exactitud del texto traducido. Por favor, tenga en cuenta que algunas aplicaciones y/o servicios pueden no funcionar como se espera cuando se traducen.
Português
Inglês é o idioma de controle desta página. Na medida que haja algum conflito entre o texto original em Inglês e a tradução, o Inglês prevalece.
Ao clicar no link de tradução, um serviço gratuito de tradução será ativado para converter a página para o Português. Como em qualquer tradução pela internet, a conversão não é sensivel ao contexto e pode não ocorrer a tradução para o significado orginal. O serviço de Extensão da Carolina do Norte (NC State Extension) não garante a exatidão do texto traduzido. Por favor, observe que algumas funções ou serviços podem não funcionar como esperado após a tradução.
English
English is the controlling language of this page. To the extent there is any conflict between the English text and the translation, English controls.
Clicking on the translation link activates a free translation service to convert the page to Spanish. As with any Internet translation, the conversion is not context-sensitive and may not translate the text to its original meaning. NC State Extension does not guarantee the accuracy of the translated text. Please note that some applications and/or services may not function as expected when translated.
Collapse ▲The planting method, rate, and timing used for cover crops will depend on a farm’s goals, rotation, equipment, and other practices. Growers need to determine which planting practices best suit their operation while also allowing them to establish a cover crop properly to enhance its benefits.
Planting Methods
Broadly speaking, the three main methods for planting cover crops are drill, ground broadcast, and aerial seeding. Selecting a method will depend on the equipment you have or are willing to purchase, the harvest dates of the previous cash crop, and the cover crop species being planted.
Drill
Particularly successful in a no-till management system, drill seeding is often the most consistent method that provides improved uniformity and seed-to-soil contact. This method would take place after the harvest of the previous cash crop.
Improved seed-to-soil contact allows growers who use a drill seeder to plant at lower rates than the other methods and still get even stands. While this method often has lower seed costs, the time and equipment required can increase overall planting costs. Growers relying on this method may have more difficulty planting cover crops by the recommended dates after a late harvested cash crop.
Ground Broadcast
Broadcasting can often be a quicker and simpler method for planting cover crops. Several equipment options allow growers to broadcast their cover onto a field. However, getting reliable seed-to-soil contact with many of these methods can be challenging, diminishing a cover crop’s establishment and performance in the field. Increased seeding rates are often recommended, which creates additional costs for growers.
Incorporating seeds with broadcasting can improve seed-to-soil contact, providing an additional option for growers practicing tillage. Some incorporation may be necessary for larger-seeded cover crops, but broadcasting generally works best with small-seeded cover crops.
Aerial Broadcast
Aerial seeding a cover crop may be the fastest method and is often done by a contractor. However, it is important to consider the experience of an aerial applicator since flying on cover crops can present unique challenges. Again, higher seeding rates are recommended for this method to achieve an adequate cover crop stand.
Aerial seeding with drones is growing in popularity and may become an option for growers statewide. Drones can fly closer to the ground and better handle obstacles like tree lines, allowing for improved planting. However, smaller seedboxes and the need to recharge batteries add additional time to planting.
Planting Rates
Recommended cover crop seeding rates will vary depending on the species, farm location, and planting method. Finding the most localized seeding rate for your farm is a good practice. Farmers involved in a cover crop incentive program should note that most programs have seeding rate requirements. It is imperative to follow these guidelines to remain eligible for incentives.
Planting at appropriate rates can be crucial for adequate biomass and ground cover to enhance cover crop benefits. Growers must decide whether enhanced benefits from higher rates are worth the additional costs.
Planting Dates
Planting cover crops by the recommended dates is crucial for proper establishment, stand, and biomass. Ensuring this can significantly improve the benefits of cover crops and overall success. Planting dates will vary depending on species and location. Again, finding the most localized recommendations is beneficial.
Overcoming Late Harvests
Late or delayed crop harvest may prevent fields from being open to plant a desired cover crop species by its recommended date. While this may be less of a concern here in the southeast due to our climate, options exist for growers facing this challenge.
Interseeding or overseeding can take place before the harvest of a cash crop. High clearance ground or aerial broadcasting can allow farmers to plant a cover into a standing crop. This gives the advantage of establishing the cover crop on time but often utilizes less reliable methods.
In general, small-seeded cover crops work best and are overseeded into a cash crop whose canopy has opened. The success of these methods also relies on adequate and timely rains for proper germination.
Resources for Planting Rates and Dates
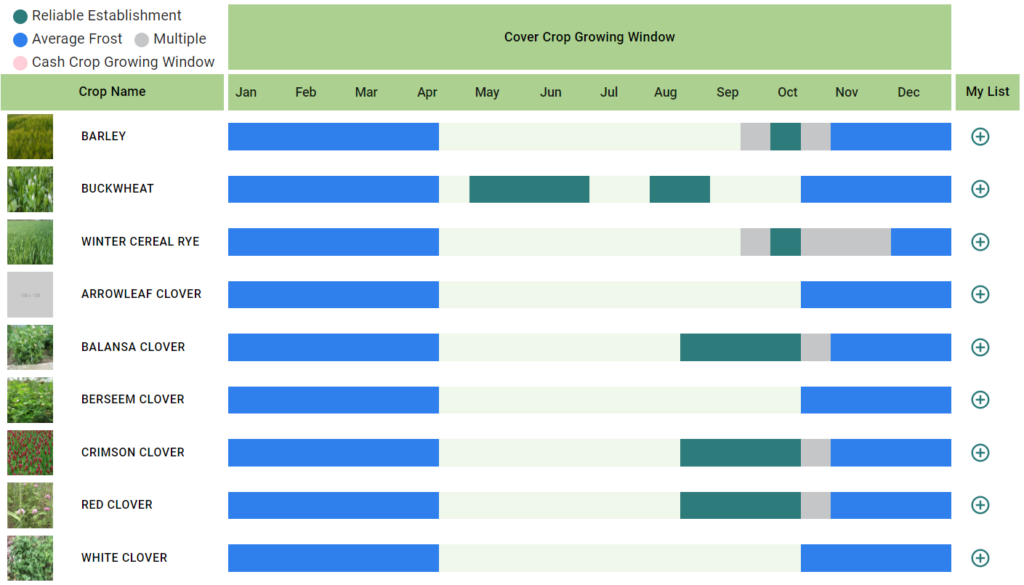
Cover Crop Selector Tool
The Cover Crop Selector Tool is an online tool from Precision Sustainable Agriculture that provides planting date recommendations based on location and species.
Farmers can compare cover crop planting dates with their cash crop rotation to see which species best fits their operation.
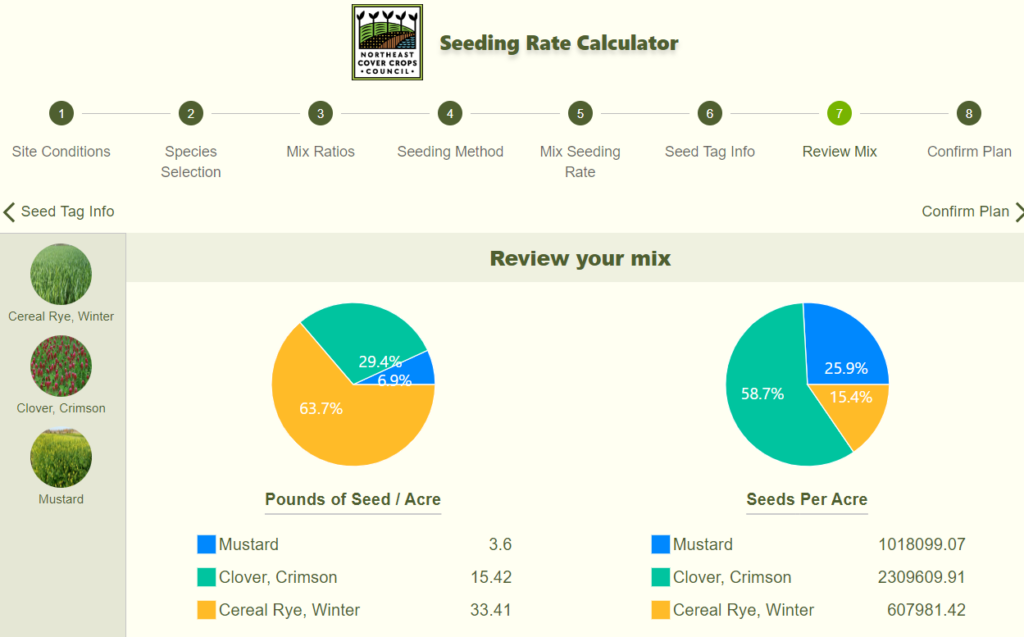
Cover Crop Seeding Rate Calculator
The Cover Crop Seeding Rate Calculator is an online tool from Precision Sustainable Agriculture that provides seed rate recommendations based on location, species, acreage, dates, planting method, and other factors.
This tool also aids farmers in developing a seed ratio for cover crop mixes to achieve their goals.
NRCS
Yourlocal NRCS office provides recommended planting rates and dates for common cover crops in your area. These rates are based on Code 340, which is the guideline for programs that incentive cover crop practices.
Seed Retailers
Cover crop seed retailers often offer recommended rates and dates for the varieties they offer, making them another valuable resource for growers.
Other Farmers
Fellow farmers with experience can often be the best resource for cover crop management recommendations. Speak with other farmers in your area to discuss possible cover crop planting rates and dates.
References
- Dorsey, N., Pekarek, K., Koehler-Cole, K., & Rees, J. (2022, September 1). Comparing Cover Crop Planting Methods. CropWatch. https://cropwatch.unl.edu/2022/comparing-cover-crop-planting-methods
- Gaskins, J., Parks, D., Wszelaki, A., & Davis, J. (n.d.). Planting cover Crops | Southern Cover Crops Council. https://southerncovercrops.org/cover-crop-resource-guide/vegetables/mountains-ridge-valley-piedmont/planting-and-managing-cover-crops/planting-cover-crops/
- Kientzy, D., Ellis, C., & Massey, R. (2023, October). Selecting Cover crop seeding machinery | MU Extension. https://extension.missouri.edu/publications/g1209
- Licht, M. (2019, July 23). A Look at Cover Crop Seeding Methods | Integrated Crop Management. https://crops.extension.iastate.edu/blog/mark-licht/look-cover-crop-seeding-methods